Lithium Ion Batteries vs. Graphene Batteries
With fast-paced advanced technology, not only our technological gadgets like televisions or phones but also our vehicles and even our homes have evolved to be digital and intelligent in the past decade. Thus, we are relying on and becoming more dependent on power supply sources. In terms of power supplies, lithium-ion batteries are supreme for the time being, but this technology also seems to be changing.
Now, there are multiple options available in the market, like Graphene batteries and upgrade one. To know which one is better for you, read this article, as we'll discuss the war of Lithium-Ion Batteries vs. graphene Batteries.
Lithium Ion Batteries vs. Graphene Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries use two conductive plates coated in a porous material and enclosed in an electrolyte solution, just like Graphene batteries. However, these two batteries have different qualities, features, and outcomes. So keep reading to choose the best.
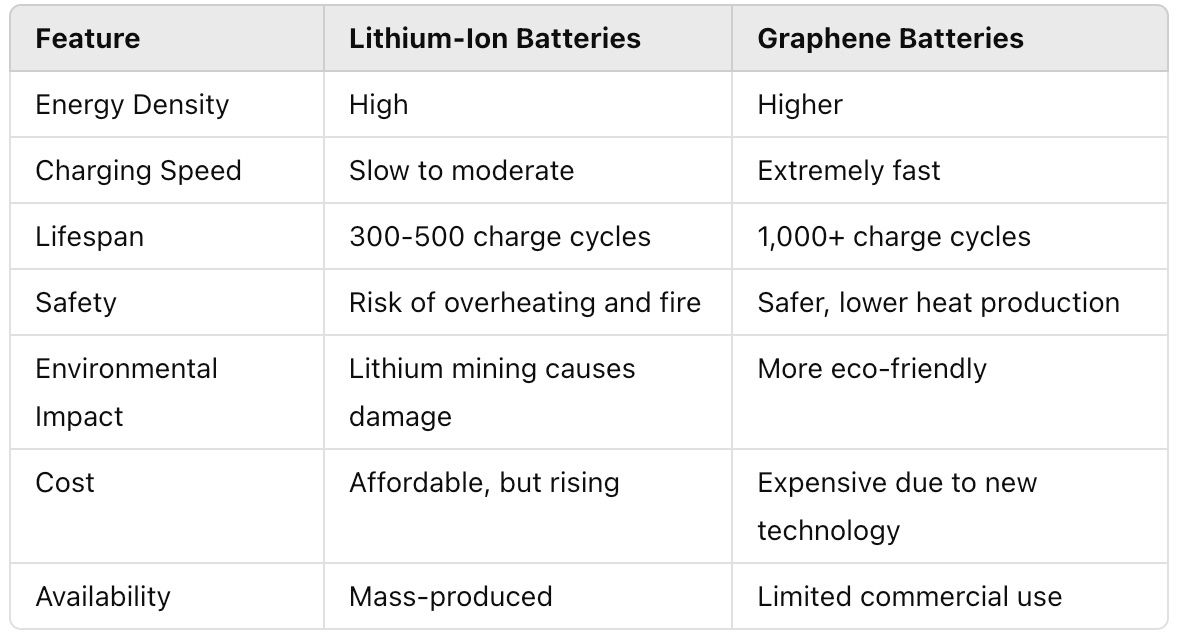
1.Safety
Graphene batteries have five times more energy density than normal lithium-ion batteries, so they are Graphenendeed, lithium-ion batteries also have high safety features, but there have been a few significant risks of potential damages, like thermal runaway and overheating.
Runaway chemical fluctuations in lithium-ion batteries can cause fire due to overcharging, puncturing, or overheating. Graphene batteries are significantly less prone to such problems and are highly stable, strong, and flexible.
2.Electrical Conductivity
In a different table, lithium-ion batteries have poor electrical conductivity than graphene batteries. This makes it possible for graphene batteries to deliver a massive amount of current while also charging fastly.
For instance, fast device-to-device charging or high-capacity automotive batteries can benefit from this. High heat conduction also makes the cells operate cooler, avoiding heating and increasing their lifespan even in tiny cases.
3.Weight
Compared to Lithium-ion batteries, Graphene batteries are thinner and lighter in weight. These graphene batteries come with more compact, slimmer, and higher capacities that do not need additional space.
Furthermore, graphene batteries can reserve more than 1000 Wh of energy per kg, while lithium-ion batteries can only store up to 180 Wh.
4.Cost
Because of higher manufacturing costs and production, lithium-ion batteries are nearly 40% more expensive than other batteries.
On the other hand, Graphene is alGraphenetle pricey. A few years back, the cost of Graphene was mGraphene gold, making it highly expensive for an average customer. Further, Graphene manufacturing still needs to grow and scale up, so it's a little pricey.
5.Energy Density
Graphene has a higher energy density than lithium-ion batteries. Li-ion batteries store up to 180 Wh per kilogram, while Graphene can rGraphenebout 1000 Wh per kilogram. As a result, a graphene battery can pack with massive capacity, and the same side as a lithium battery is real.
Advantages of Graphene Batteries and Lithium Ion Batteries
Advantages of Graphene Batteries
- Due to its honeycomb design, it is a strong conductor of electrical energy, making it charge more quickly than lithium-ion batteries.
- In comparison with lithium-ion batteries, Graphene has mGraphenegy density.
- Graphene batteries support in severe weather conditions.
- These batteries are more robust and flexible than other lithium-ion batteries.
Advantages of Lithium Ion Batteries
- Lithium-ion batteries are available in multiple types and sizes to use effectively in numerous applications.
- These batteries need little to no maintenance to operate.
- A voltage of 3.6 volts is produced by each lithium-ion battery, which is higher than other battery types.
Key Differences of Lithium Ion Batteries and Graphene Batteries
Applications of Lithium Ion and Graphene Batteries
Lithium Ion Batteries
Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, tablets, and cameras
Electric Vehicles: Cars, buses, and bikes
Energy Storage Systems: Solar energy storage, backup power for homes and businesses
Graphene Batteries
Electric Vehicles: Faster charging and longer ranges could make graphene batteries a key player in the EV market
Wearables and Portable Devices: Due to their light weight and efficiency, graphene batteries are well-suited for small electronics
Energy Storage: Large-scale applications such as grid energy storage could benefit from the enhanced capabilities of graphene batteries.
Is Graphene Batteries Better Than Lithium-Ion Batteries?
You are not restricted to either graphene or lithium-ion batteries.
Graphene can optimize the cathode conductor performance in lithium-ion batteries, which are indicated as Graphene-metal oxide hybrids or graphene composite batteries.
Compared to present batteries, hybrid batteries are slimmer, lighter, and quickly charged. They last longer and offer high storage capacity. Among the multiple graphene-baGrapheneery types and technologies, graphene lithium-ion batteries will be used in 1-3 years, but Graphene is anticipated to be used in 10 years.
These are cheaper and easier to recycle than lithium-ion batteries. So, choose the best for you and schedule a meeting with Innotinum to replace old-school batteries.
Bottom Line
Future EVs may use Graphene aluminium-ion batteries as their primary power source because they can charge 60 times earlier than Lithium-ion batteries and supply much more energy than pure aluminium cells. For example, Graphene aluminium-ion cells can recharge the battery in a minute and a coin-cell battery in a few seconds.