Inverter vs Rectifier - Which One Do You Need?
Inverters and rectifiers are famous electronic circuits that alter the current level and convert it from one form to another. Both devices play a crucial role in power management, making it difficult for householders to choose one.
Let's review the essential knowledge about inverters and rectifiers to ensure that you choose the right options.
What are inverters?
Inverters are devices attached to most renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines. They work by observing the direct current generated from the source and converting it into an alternate current before supplying it to the batteries.
Inverters come in multiple types, such as:
●Square wave inverters: Produces square-shaped AC waves.
●Modified sine wave inverters: Generate sine waves by using available energy. They are frequently used in power tools and household appliances.
●Pure sine inverters: Produce current waves continuously and apply them to the grid attached.
●Grid-tie inverters: These are used in renewable energy systems as they can easily be attached to the grid.
●Off-grid inverters: Don't get connected with the electrical system. Ideal for remote areas.
●Hybrid inverters: A combination of off-grid inverters and Grid-tie inverters.
How does an inverter work?
When the inverter is switched on, power between positive and negative patterns is created. Then, these pulses are filtered and completely smoothed from the sinusoidal waveform.
However, the frequency output depends entirely on the switching speed and input voltage your inverter supports. Lastly, the AC waves are transformed into DC in numerous forms, such as square, triangular, modified sines, etc.
Applications of inverters
Here are all the significant contributions of inverters in varied fields.
1.Portable power: Inverters enable the use of AC appliances. They convert the current from DC to AC for multiple off-grid applications, such as EVs and boats, thus allowing for greater comfort and enhanced convenience.
2.In UPS systems: During power cuts, inverters in UPS help the batteries store power as a backup.
3.Renewable energy systems: Inverters facilitate the conversion of DC power generated by solar panels and wind turbines into usable power, thus ensuring an efficient utilization of the source.
4.In-households: Inverters can be easily attached to the solar system in any household with less space. They help households be independent and operate appliances without the official grid connection.
5.Electric vehicles: Inverters help convert the current from DC into AC so that the batteries of EVs can be charged. You get enhanced comfort by driving the cars for long routes without recharging every few miles.
Benefits of inverters
1.Versatility: Inverters are highly versatile. The alternate current generated by these can be used in an extensive range of devices and appliances.
2.Integration with renewable energy: Inverters help you better utilize energy resources. Whether it is wind turbines or solar panels, you can attach them to any to produce energy and become self-sufficient.
3.Backup power: The inverters help in power outages by storing energy in the batteries.
What are rectifiers?
Rectifiers are a form of converter that converts alternate current into direct current. It is an essential component to have for most electronic devices. These are usually used in power supplies, battery chargers, etc. There are different types of rectifiers, including:
1.Half-wave Rectifier: This device passes half of the AC waves and blocks the other half. It is frequently used in areas with low power needs.
2.Full-wave Rectifier: The full-wave Rectifier uses all the AC waves and doubles the frequency in the overall output of DC.
3.Bridge rectifier: The diodes of such rectifiers are arranged in the bridge form. It converts entire AC wavers into DC generated by the source.
4.Centre-tap rectifiers: These use a centre-tapped transformer that acts as the neutral point of both diodes. They are frequently used in applications using dual-polarity power.
5. Controlled Rectifier: Also known as the thyristor rectifier, this controls output volts and adjusts the firing angle during the process.
How does the rectifier work?
The Rectifier blows the flow of current from one direction. Thus forcing it to flow in a singular direction.
It might use diodes for such a process. A simple rectifier uses one or two diodes for the conversion. Nevertheless, the final results of the outfit depend upon the type of Rectifier you are using. Furthermore, the output can be controlled through the capacitors and resistors.
Applications of rectifiers
Following are some of the significant applications of rectifiers in multiple fields
1.Power supplies: Rectifiers play a crucial role in power supplies. They convert the alternate current into direct current to make the electronic devices work. In addition, they ensure a stable supply of the DC voltage.
2.Battery charging: Rectifiers convert the AC into DC to charge the batteries without any safety risk. Thus, they ensure that the batteries are charged effectively and that their lifetime isn't compromised.
3.Telecommunication: Rectifiers facilitate telecommunications by supplying the required voltage for effective transmission.
Benefits of rectifiers
1.Efficient power conversion: You can use the rectifiers to convert power efficiently and safely.
2.Cost-effectiveness: The rectifiers are cost-effective for converting alternate current into direct current.
3.Helps to operate machines: Rectifiers power multiple machines and systems in the industrial sector.
Inverters vs rectifiers- which one should I choose?
Well, both inverters and rectifiers have their benefits to offer. However, going with the inverters is a good choice for a general household.
If you are dealing with renewable energy systems and need a Portable backup, powers and inverters can only help you with that. In addition, they convert the DC into AC, which most electrical devices and appliances require. However, getting it from a reliable source would only benefit.
Innotinium, with four years of experience, offers an extensive range of inverters with different capacities.
The range includes:
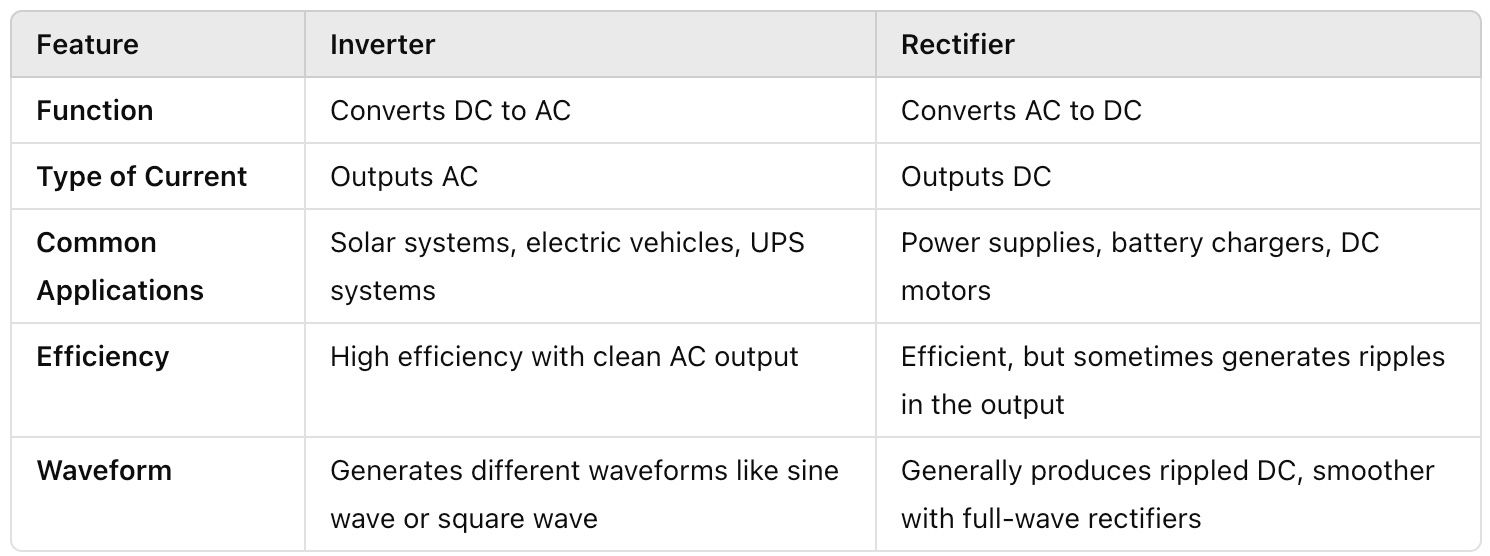
Key Differences Between an Inverter and a Rectifier
Now that you have an idea of what inverters and rectifiers do, let’s dive into a more detailed comparison of their key differences:
Which One Do You Need?
Choosing an Inverter
If your goal is to run devices that require AC power, and you’re working with DC power sources (like solar panels or batteries), you will need an inverter. For example:
- In solar power systems, you’ll need an inverter to convert the DC electricity from your solar panels into AC power to run your appliances.
- In backup power systems like a UPS, an inverter is necessary to supply AC power when the main electricity supply is down.
Choosing a Rectifier
If you are working with an AC power source and need to convert it to DC to power your devices or charge batteries, a rectifier is what you need. For example:
- In battery charging systems, rectifiers are used to convert AC from the electrical grid into DC for charging.
- In electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and power supplies, rectifiers are essential to ensure that the AC from the grid is converted to usable DC.
When Might You Need Both?
In some cases, you might need both an inverter and a rectifier. This is common in power systems that work with both AC and DC currents. For example, a solar power system might require a rectifier to convert AC from the grid into DC for storage, and then an inverter to convert stored DC back into AC for use in your home. In uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), a rectifier may be used to convert AC to DC for battery charging, while an inverter is used to convert the DC from the battery back to AC in the event of a power failure.
Conclusion
To sum up, inverters and rectifiers offer different sets of prepositions, making it difficult for a common household to choose one.
That is why we have formed this guide, which talks about some of the essential factors of both services to help you decide better.
You can also find applications, benefits, and types of both devices to accurately reach a well-suited conclusion.
Related blog: How to fix inverter overload problems