Inverter Generator Vs. Generator: Which Is Best for Home Use?
In today’s world, having a reliable power source is essential, especially when the grid fails or during emergencies. Two of the most common options for backup power are inverter generators and traditional generators. But which one is better for home use? That’s the question we’re going to explore in this comprehensive guide.
Let’s break down the key differences, pros, and cons of inverter generators and traditional generators to help you make an informed decision for your home.
What Is a Traditional Generator?
A traditional generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. These generators use an engine to power a rotating alternator, which generates electricity. Most traditional generators run on gasoline or diesel and are known for their ability to produce large amounts of power. They’re widely used for both residential and commercial purposes.
Advantages of Traditional Generators
Power Output: Traditional generators generally provide a higher power output compared to inverter generators. This makes them suitable for running multiple appliances or heavy-duty equipment at once.
Durability: Built to handle tough conditions, traditional generators are known for their robustness and long-term reliability.
Fuel Availability: Gasoline and diesel are widely available, making traditional generators easier to fuel in emergencies.
Disadvantages of Traditional Generators
Noise Levels: Traditional generators are notorious for being loud. If noise is a concern, this could be a major drawback.
Fuel Efficiency: These generators tend to burn more fuel than inverter generators, leading to higher running costs.
Size and Portability: Traditional generators are usually bulkier and heavier than their inverter counterparts, making them less portable.
What Is an Inverter Generator?
An inverter generator is a more recent innovation in the world of portable power generation. It uses advanced electronics to produce cleaner and more stable power. Inverter generators work by converting raw power into a steady, consistent output that’s ideal for sensitive electronics.
Advantages of Inverter Generators
Cleaner Power: The primary benefit of an inverter generator is that it produces cleaner power. This makes it safe for sensitive electronics like laptops, phones, and TVs, which could be damaged by the power fluctuations from a traditional generator.
Quiet Operation: Inverter generators are much quieter than traditional generators. They have noise-dampening features and operate at lower decibel levels, making them perfect for residential areas.
Fuel Efficiency: Inverter generators adjust their engine speed based on the power demand. This means they only use as much fuel as needed, leading to better fuel efficiency.
Portability: Thanks to their compact size and lightweight design, inverter generators are easy to transport and store.
Disadvantages of Inverter Generators
Lower Power Output: While inverter generators are great for home use, they usually don’t provide the same amount of power as traditional generators. This can be a limitation if you need to run several heavy-duty appliances simultaneously.
Higher Initial Cost: Inverter generators can be more expensive than traditional generators, especially for those with higher power outputs.
Not Ideal for Long-Term Use: While inverter generators are efficient and quiet, they may not be the best choice for long-term, continuous operation in high-demand situations.
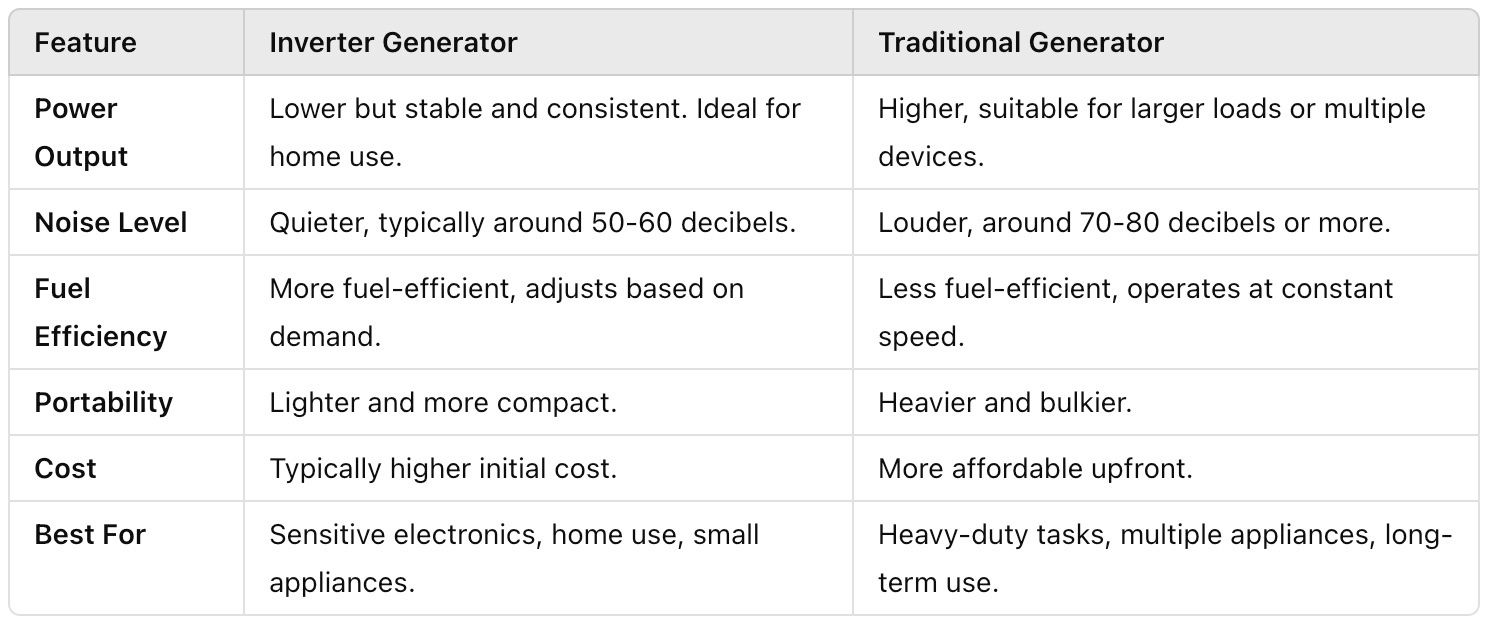
Key Differences Between Inverter Generators and Traditional Generators
To help you make a better comparison, here are some key differences between inverter generators and traditional generators:
Which One is Better for Home Use?
The answer depends on your specific needs. Let’s break it down:
1. Inverter Generator for Home Use
If you’re looking for something to power a few essential devices in your home, such as lights, refrigerators, or even a few electronics like your TV and phone, an inverter generator is likely the best choice. They are perfect for homeowners who want a quiet, fuel-efficient, and portable option for occasional power outages or outdoor activities.
Best for: Homeowners with sensitive electronics, small to medium power needs, or those who prioritize noise reduction and fuel efficiency.
2. Traditional Generator for Home Use
If you live in an area with frequent power outages or need to run multiple heavy-duty appliances (like air conditioners, water heaters, or large power tools), a traditional generator might be the better option. Traditional generators are better suited for powering multiple devices at once and for long durations.
Best for: Larger homes, longer power outages, or those with significant power demands (multiple air conditioners, large appliances, etc.).
Considerations When Choosing Between an Inverter Generator and a Traditional Generator
Power Needs
Think about the amount of power you need. If you just need to keep a few devices running during a power outage, an inverter generator will be sufficient. But if you need to power multiple large appliances simultaneously, a traditional generator is more appropriate.
Noise Level
If you live in a residential area and are concerned about noise, the quieter operation of an inverter generator makes it the better choice. Traditional generators are much louder and can disturb your neighbors.
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel consumption is another consideration. Inverter generators are more fuel-efficient, which can save you money over time. Traditional generators tend to consume more fuel since they run at a constant speed, regardless of the load.
Budget
Inverter generators typically come with a higher initial cost compared to traditional generators. However, their fuel efficiency and quieter operation can justify the price in the long run, especially if you use it regularly for home use.
Maintenance and Durability
Traditional generators are usually built to handle heavy loads and can be more durable for long-term, intensive use. Inverter generators are perfect for shorter, less demanding operations but may not be as robust in the long run, especially if subjected to heavy use.
Conclusion
Ultimately, choosing between an inverter generator and a traditional generator boils down to your specific needs, preferences, and budget. If you’re looking for a reliable, quieter, and more efficient power source for basic home use, an inverter generator may be your best bet. However, if you need to power multiple large appliances or require long-term power, a traditional generator will serve you better.
When making your decision, keep in mind the factors discussed above and choose the generator type that aligns best with your home’s power requirements. Whether you opt for the fuel efficiency and quiet operation of an inverter generator or the raw power of a traditional generator, both options provide invaluable backup power in times of need.
Related blog: Inverter vs Rectifier Efficiency: What to Know About Power Losses and Performance