How to Choose the Right Battery System for Your Home?
Transitioning to home battery storage is a game-changer for energy independence, cost savings, and environmental impact. With more people exploring energy storage, the question, "How to choose the right battery system for your home?" is top of mind. Whether it’s for backup power, managing solar energy, or offsetting electricity costs, the right battery system can help you take control of your power usage. In this guide, we’ll walk through everything you need to know to make a smart, confident choice for your home.
Why Home Battery Systems Are Becoming Essential
As electricity costs rise and power reliability fluctuates, many homeowners are considering batteries to store and manage energy. With solar systems becoming more accessible, battery storage allows homes to store excess solar power and use it when electricity prices peak or during outages. Having a reliable home battery system can mean uninterrupted power, greater energy independence, and more control over energy expenses. But with many options available, understanding which type suits your home is essential.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Home Battery System
1. Understand Your Power Needs
The first step in selecting the right battery is to analyze your home's energy needs. Here’s how to approach it:
Check Your Daily Energy Usage: Most utility bills provide a breakdown of daily or monthly usage. Use these numbers as a baseline for your battery’s storage needs.
Estimate Your Backup Requirements: Decide which appliances or systems you’ll need during an outage. Essential items like refrigerators, lighting, and heating should take priority. This helps determine your ideal battery capacity.
Consider Seasonal Changes: If your home uses more energy in winter or summer, factor these peaks into your calculations.
2. Battery Capacity and Power Rating
Battery systems are rated by two main factors: capacity (kWh) and power rating (kW). Let’s break it down:
Capacity: This is the total amount of electricity the battery can store. Higher capacity means more power stored but doesn’t necessarily mean you can use all of it at once.
Power Rating: This indicates how much electricity the battery can deliver at once. Batteries with higher power ratings can support multiple appliances simultaneously, whereas lower ratings are best for a few essential devices.
A balance between capacity and power rating is crucial. A high-capacity battery with a low power rating might store enough energy for your needs but may struggle to power larger appliances.
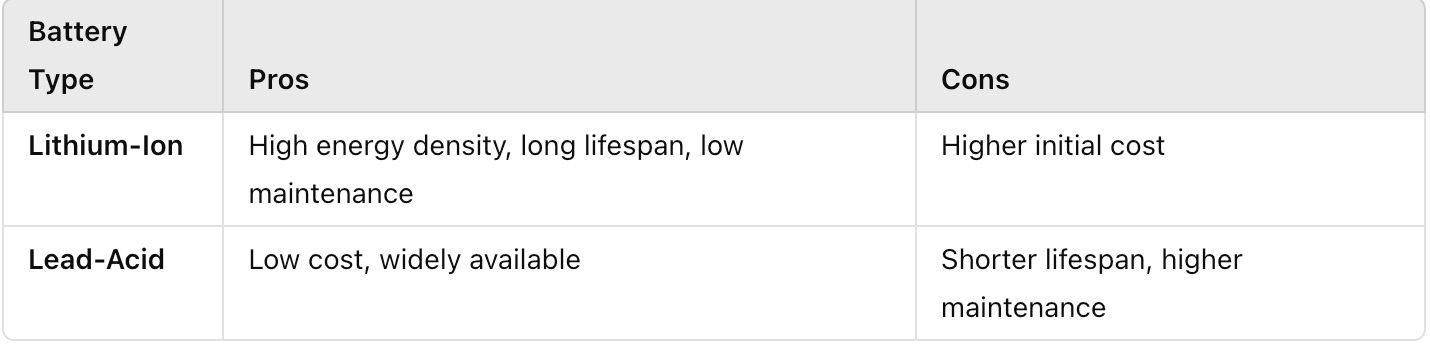
3. Battery Chemistry: Lithium-Ion vs. Lead-Acid
Battery chemistry plays a big role in performance, lifespan, and maintenance. Let’s examine the two most common types:
Lithium-Ion: Known for efficiency, durability, and lightweight design, lithium-ion batteries are currently the top choice for home storage. They offer higher energy density, meaning they can store more power without taking up much space. They’re also low-maintenance and have a longer lifespan.
Lead-Acid: Lead-acid batteries are less expensive and have been in use for years. While reliable, they require more maintenance, offer less capacity, and have a shorter lifespan. For homes with limited energy needs and budget constraints, lead-acid can be a workable option.
Choosing the right chemistry depends on your priorities—whether it's maximizing lifespan, reducing maintenance, or keeping costs low.
4. Depth of Discharge (DoD)
Depth of Discharge (DoD) indicates how much of a battery's capacity can be used before recharging. Most batteries list a DoD percentage, with higher DoD allowing for more usable energy:
Higher DoD: Lithium-ion batteries usually have a higher DoD (around 80-90%), allowing you to access more of the stored power.
Lower DoD: Lead-acid batteries have a lower DoD (around 50%), so they need more frequent recharging to avoid damage.
Choosing a battery with a higher DoD means more power for your home before needing a recharge, which can be more efficient in the long run.
5. Battery Lifespan and Cycle Count
The lifespan of a battery system is typically measured in cycles—the number of times a battery can be charged and discharged.
Cycle Count: Higher cycle count means the battery lasts longer. Lithium-ion batteries generally have a higher cycle count than lead-acid batteries, offering a longer lifespan.
Expected Years: Most lithium-ion batteries last between 10-15 years, while lead-acid batteries generally last around 5-7 years.
Consider the cycle count and lifespan if you’re looking for a long-term solution. A battery with a higher cycle count may cost more upfront but provides value over time.
6. Inverter Compatibility
Inverters are crucial for converting the direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) that powers your home. There are two main types of inverters:
Hybrid Inverters: These work well with both solar panels and batteries, making them ideal for solar-powered homes.
Battery-Specific Inverters: Designed solely for battery systems, these may be better if your system doesn’t integrate solar.
Choose an inverter compatible with your battery type, and if possible, look for inverters that support both battery and solar inputs for flexibility.
7. Cost and Financing Options
Battery systems vary widely in price. Here’s what to keep in mind:
Initial Costs: Prices range based on capacity, battery type, and brand. A lithium-ion battery setup will cost more than a lead-acid system but offers longer-term value.
Maintenance Costs: Lithium-ion systems require less maintenance, reducing long-term costs.
Incentives and Financing: Many regions offer tax credits, rebates, or financing options to make battery storage more affordable. Check local and federal programs that can lower your investment.
8. Home Integration and Space Requirements
Consider the space and integration needs of the battery system:
Indoor or Outdoor: Some batteries are designed for outdoor use, while others are better kept indoors. Check for weather resistance and ventilation needs.
Space Constraints: Batteries come in various sizes. Be sure to assess how much room you can dedicate, particularly for larger setups or if planning a future expansion.
Pros and Cons of Popular Battery Types
Let’s take a quick look at some of the pros and cons of popular battery types to help narrow your choices:
Making the Final Decision: Which Battery System is Right for You?
Selecting the right battery system is all about aligning your needs with the battery’s features. Here’s a quick checklist:
List Your Essentials: Identify which appliances and systems are essential during outages.
Calculate Your Energy Usage: Use your utility bill as a guide to determine daily needs.
Set a Budget: Factor in both upfront costs and long-term savings from incentives.
Assess Space: Make sure your home has suitable space for installation.
Ultimately, the best battery system is one that aligns with your lifestyle, budget, and energy needs. For homes aiming for solar integration, prioritize hybrid systems that support both solar and battery storage. If backup power is your goal, consider capacity, power rating, and lifespan.